- VOX
- Technical Blogs
- Backup Exec
- Best Practices to Protect Hyper-V
Best Practices to Protect Hyper-V
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Virtualization is a critical component of an IT Infrastructure. It provides flexibility to create Virtual Machines (VMs), clone VMs and to deploy them at a very rapid pace in different environments. Though virtualization is very flexible, VMs still need to be protected for various reasons like Disaster Recovery, Application Failure, Patch Failure, Host Hardware Failures, Data Corruptions, Ransomware Attacks and so on.
To overcome these challenges, Backup Exec provides leading features and protection for Hyper-V host and VMs.
Before you understand more about the Backup Exec features, here are some associated terms:
What is Hyper-V?
Hyper-V is Microsoft’s virtualization platform or hypervisor which provides the capability to create and run Virtual Machines. It is critical to protect Hyper-V host components and Virtual Machines.
Backup Exec provides various options to back up and recover Virtual Machines.
How to Protect Hyper-V Virtual Machines:
- Install Backup Exec Remote Agent on the Hyper-V host.
- Select a Hyper-V host machine, create a new backup, and include the Virtual Machines to be protected.
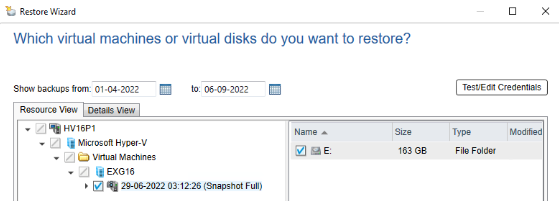
Restoring Hyper-V Virtual Machines:
- Select a Hyper-V host machine, create a new restore job, and include the Virtual Machines to be restored.
- Virtual machine can be restored to the same host, a different Hyper-V host, or to different disk paths.
Granular Recovery Technology for Virtual Machines or Application GRT (AppGRT):
AppGRT permits the recovery of Exchange, Active Directory, SharePoint, and SQL data from a virtual machine without running a separate application-level backup of these applications. Using the same Virtual Machine backup using GRT (Granular Recovery Technology), Backup Exec quiesces application to get application metadata, which is later used to restore application level granular data. For example: - Active directory user, email, mailbox, SharePoint document, SQL database, and so on.
This AppGRT feature can be enabled from the backup job.
NOTE: Remote Agent must be installed and running inside the guest VM.
Go to Backup Options >Virtual Machines >Virtual Machine Application Granular Recovery Technology Settings. The screenshot displays the available settings.
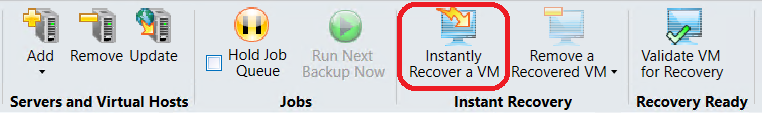
Instant Recovery of Hyper-V Virtual Machine:
With Backup Exec Instant Recovery Feature, virtual machines can be directly powered on from the backup storage. So virtual machines can be recovered instantly without waiting to transfer data from a backup.
NOTE: For more information about the requirements of Instant Recovery feature refer to the following article - Requirements for instant recovery of VMware and Hyper-V virtual machines.
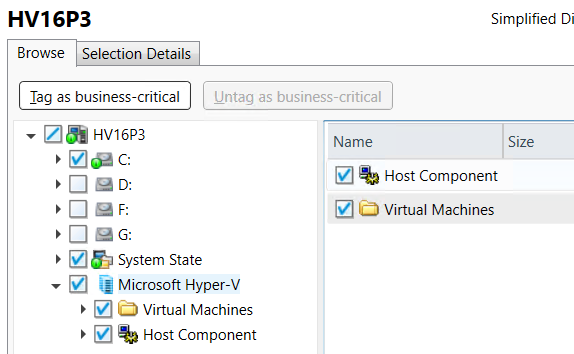
Protecting Hyper-V host / Disaster Recovery of Hyper-V host:
- Regularly back up the Hyper-V host with all the components required for disaster recovery, such as System Volume, System State, and Hyper-V Host Component.
- To recover a Hyper-V host, use Simplified Disaster Recovery disk and recover all Hyper-V host related components.
NOTE: For more information about performing disaster recovery, refer to the following article - Step by step guide for Simplified Disaster Recovery (SDR) with Backup Exec.
Forever Incremental Backup:
Backup Exec introduces Forever Incremental Backup, also known as Backup Exec Accelerator. When you create a forever incremental backup policy, a full backup is taken from the source virtual machine that is followed by incremental backups. A consolidate backup is run by consolidating the previous set of full and incremental backups. Subsequent incremental backups use the consolidate full backup as a baseline to determine changes in the source virtual machine. A consolidate full backup is equivalent to a full backup from the source virtual machine. It can be used for all types of restores, such as Virtual machine restore, GRT restore, application GRT restore, Instant Recovery, and Recovery Ready.
There are some differences between the traditional and the forever incremental backups of virtual machines.
See Differences between the traditional and the forever incremental backups of virtual machines.
Benefits of Forever Incremental backups
- Frees up the backup window.
- Meets the backup policy requirements and recovery time objectives by running weekly consolidated backups without running a full backup from the source virtual machine.
- Reduces the load on virtual machines and the network bandwidth by avoiding frequent full backups from the source virtual machine.
Resilient Change Tracking for Hyper-V Virtual Machine:
Resilient Change Tracking (RCT) based backups allow faster incremental backups. These are based on Microsoft's native change tracking mechanism which doesn't involve VSS infrastructure on Hyper-V host thereby reducing any VSS related errors during backups.
For more information about the feature, refer to - Resilient Change Tracking comes to Backup Exec
General best practices:
- Perform a periodic full backup.
- Back up to a disk-based storage device instead of a tape device to take benefit of GRT and IR.
- Ensure that each virtual machine has a unique name. If you have two virtual machines with the same display name, backup jobs may fail.
- Ensure that the correct version of the Hyper-V Integration Services is installed. The version of the Hyper-V Integration Services must match the version of Hyper-V that you use. Note that Hyper-V Integration Services cannot be disabled. Get more information about updating or keeping Hyper-V Integration Services up to date, refer Manage Hyper-V Integration Services.
- It is highly recommended to use RCT that is enabled by default instead of the other processing methods (standard and faster).
- Upgrade Backup Exec to latest version when possible. Check software and hardware compatibility before upgrade. Refer to: Backup Exec Compatibility List Home Page
- Upgrade Remote Agent on Hyper-V host and Virtual machine to latest version.
- To avoid VM’s going into a saved state, select the following option in Backup Exec job settings:
- Always perform a full backup of Hyper-V host and virtual machines before applying any operating system patches/updates.
Using SMB shares as Hyper-V storages, users can save local storage space. Refer blog: Protecting Hyper-V Virtual Machines on SMB using Backup Exec 20.4 for more details.
Backup Exec also provides a separate feature to convert physical machines to virtual machines (Hyper-V or VMware).
For more information, refer to the Backup Exec 22 Administrator’s Guide.
More Help:
If you have a problem with Backup Exec and require assistance, contact Veritas Technical Support, or join the conversation on VOX BE Community.
If you want to use a trial version of Backup Exec in your environment, go to https://www.veritas.com/form/trialware/backup-exec.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
- Understand, Plan and Rehearse Ransomware Resilience series - Strategy in Protection
- Best Practices to Protect Hyper-V in Backup Exec
- Backup Exec—The Continuous Road to Full Public Sector Compliance in Backup Exec
- It should be Cybersecurity Awareness Month—every month! in Protection
- Ransomware’s Greatest Fears: Veritas Solution Days International Tour Dates 2021/2022 in Veritas Events